
|
|
Fire Wars
|

|
|
Classroom Activities
|
Where Growth Meets Growth
|
Objective
To identify fire risk factors for a property located near a wildland
area.

-
copy of "Where Growth Meets Growth" student handout (PDF
or
HTML)
- colored pencils

-
One of the issues surrounding wildland fires involves areas
where uncontrolled urban growth meets uncontrolled vegetative
growth. People who live in these areas should take extra
precautions to limit the effects of any nearby wildland fire
that might occur. Students will take on the role of Fire Marshal
for a house that requires a safety evaluation.
-
Review with students some of the types of ecosystems that could
be subject to wildland fire under these circumstances. (See
Activity Answer for more information.)
-
Organize students into teams and distribute a copy of the "Where
Growth Meets Growth" student handout and colored pencils to each
team.
-
Have students identify, number, and provide reasons for areas of
increased risk they think should be changed. Have students
consider changes that may mean adding or taking something away
from the property that is not currently featured in the
illustration.
-
When teams are finished, compile everyone's results on the
chalkboard, categorize the measures, and review them. What are
the benefits of these changes? Which changes would students make
first and why?
-
As an extension, have students survey and identify areas of
their towns that may be most at risk for fire.

The following are some measures that can be taken to protect a house
from wildland fire.
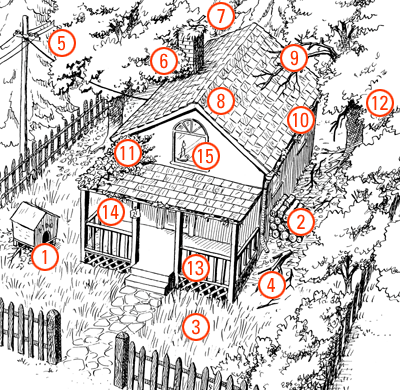
-
Remove leaves and rubbish under doghouse and any other
structures.
-
Stack firewood at least 100 feet away and uphill from the house.
-
Water and mow grass regularly to keep it green and less
flammable.
-
Rake flammable vegetation such as dead leaves, limbs, branches,
twigs, and grass clippings.
Have power company clear branches from lines. -
Prune tree branches within 15 feet of a chimney outlet.
Clean chimneys at least once a year. -
Make sure roof uses fire-resistant materials such as asphalt,
fiberglass, concrete tile, clay tile, or metal.
Remove dead branches that extend over the rooftop. Clean gutters regularly. Remove vines from exterior walls. Arrange trees so that there are gaps in the canopy. -
Any part of property that includes wood, such as fence,
latticework, or facing should be changed. Alternatives include a
stone fence, brick or concrete as a porch front and, concrete or
clay tiles on the house dormer.
-
Address should be clearly posted for firefighters to see.
Never leave a flame burning unattended.
Additional measures
-
Situate the house on flat land; the steeper the slope, the
faster the fire will move up it.
-
Make sure there is open access for firefighters to reach the
property.
Plant fire-resistant shrubs and vegetation. Add an independent water supply. Add a swimming pool.

Books
Dilsaver, Larry, and William Tweed.
Challenge of the Big Trees: A Resource History of Sequoia and
Kings Canyon National Parks.
Tucson, AZ: University of Arizona Press, 1991.
Presents an environmental history of the giant sequoias and explores
the role of fire and the issue of biological conservation. Includes
maps and an annotated bibliography.
Fuller, Margaret.
Forest Fires: An Introduction to Wildland and Fire Behavior,
Management, Firefighting, and Prevention.
New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1991.
Provides an introduction to forest fires and fire ecology.
Junger, Sebastian.
Fire.
New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 2001.
Describes raging forest fires in the Western United States and other
dangerous situations at home and abroad.
Leschak, Peter M.
Hellroaring: The Life and Times of a Fire Bum.
East Peoria, IL: North Star Press of St. Cloud, Inc., 1994.
Chronicles the author's adventures as a forest firefighter.
Maclean, John N.
Fire on the Mountain.
New York: William Morrow and Co., 1999.
Depicts and analyzes the deadly 1994 fire at Storm King Mountain.
Maclean, Norman.
Young Men and Fire.
Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1993.
Describes the disaster at Mann Gulch in 1949; considered a classic
in firefighting.
Patent, Dorothy Hinshaw.
Fire: Friend or Foe.
New York: Clarion Books, 1998.
Discusses the pros and cons of fire on the ecosystem and examines
differing views and policy recommendations about firefighting and
controlled burning.
Pyne, Stephen J.
Fire in America: A Cultural History of Wildland and Rural
Fire.
Seattle: University of Washington Press, 1997.
Chronicles the history of fire in the United States; the first of
six books in the author's Cycle of Fire series.
Pyne, Stephen J.
Fire on the Rim: A Firefighter's Season at the Grand Canyon.
Seattle: University of Washington Press, 1995.
Presents a firsthand account of the author's firefighting days.
Pyne, Stephen J.
Year of the Fires: The Stories of the Great Fires of 1910.
New York: Viking, 2001.
Describes the Great Fires of 1910 through eyewitness accounts of the
rangers, soldiers, politicians, bureaucrats, scientists, and
civilians; and shows how virtually all modern firefighting policies
originated from the experiences of 1910.
Sholly, Dan R. and Steven M. Newman.
Guardians of Yellowstone: An Intimate Look at the Challenges of
Protecting America's Foremost Wilderness Park.
New York: William Morrow and Company, Inc., 1991.
Describes the fight to protect the land and people of Yellowstone
National Park during the forest fires of 1988.
Taylor, Murray A.
Jumping Fire: A Smokejumper's Memoir of Fighting Wildfire.
New York: Harcourt, Inc., 2000.
Recounts the author's 20 years of fighting wildfires in the American
West.
Web Sites
NOVA Online—Fire Wars
http://www.pbs.org/nova/fire/
Provides program-related articles, interviews, interactive
activities, and other resources.
Earth Observatory
http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Newsroom/MediaResources/Wildfires/
Shows view of wildland fires from space.
Employment and Careers in Forestry
http://forestry.about.com/cs/employment/
Lists employment opportunities in the areas of forestry and natural
resources, including an article about finding firefighting
employment online.
Fire & Aviation Fire Reports
http://www.fs.fed.us/news/fire/
Provides daily fire reports from agencies such as the National
Interagency Fire Center, the U.S. Forest Service, and the National
Park Service. Also includes archived monthly situation reports
dating back to 1994.
Fire Ecology
http://www.nps.gov/fire/fire/ecology/docs/toc.html
Includes background information about fire ecology, a Teacher's
Guide with activities and quizzes, and a glossary of fire terms and
additional references.
Fire Globe
http://www.fire.uni-freiburg.de/
Includes links to global, regional and national fire weather and
climate forecasts; near-real time global fire data; and
international forest fire news.
Fire Management Today
http://www.fs.fed.us/fire/planning/firenote.htm
Provides online issues of Fire Management Today. Topics include
wildland fire in communities, wildland fire prevention, wildland
fire weather, the role of fire in wildlands, and more.
Fire Management Tools Online
http://fire.org/perl/tools.cgi
Provides access to a collection of documentation, visuals, graphics,
notices, and software contributed by and for the wildland fire
management community.
FireNet
http://www.nps.gov/fire/index.htm
Offers information about wildland fire training and employment with
the National Park Service and provides links to other National Park
Service sites that contain specific park-related fire information.
Firewise
http://www.firewise.org/fw99/home.html
Includes daily National Interagency Fire Center Incident Management
Situation Report, peak fire seasons map, materials for educators,
and more.
Forestry
http://forestry.about.com/mlibrary.htm
Offers information about forest fires and prescribed burning.
National Interagency Fire Center
http://www.nifc.gov/
Features wildland fire statistics, current wildland fire
information, and other useful links.
Wildfire News
http://www.wildfirenews.com/
Offers information about fire ecology, a fire danger map, regional
reports, and links to additional resources. The section "So You Want
to Be a Wildland Firefighter?" highlights some of the qualifications
for a career in fighting wildland fires.
Wildland Fire in Yellowstone
http://www.nps.gov/yell/technical/fire/index.htm
Provides history and ecology of wildland fires in Yellowstone.
Wildland Fire Operations
http://www.fs.fed.us/fire/
Describes the different command operations used for a fire that
falls under more than one agency's jurisdiction. Also includes
information about hotshot and helitack crews, smokejumper
operations, and more.

The "When Growth Meets Growth" activity aligns with the following
National Science Education Standards:
Grades 6-8

|
Science Standard F:
Science in Personal and Social
Perspectives
|

|
Natural hazards
-
Internal and external processes of the earth system cause
natural hazards, events that change or destroy human and
wildlife habitats, damage property, and harm or kill humans.
Natural hazards include earthquakes, landslides, wildfires,
volcanic eruptions, floods, storms, and even possible impacts of
asteroids.
Risks and benefits
Grades 9-12

|
Science Standard F:
Science in Personal and Social
Perspectives
|

|
Natural and human-induced hazards
-
Natural and human-induced hazards present the need for humans to
assess potential danger and risk. Many changes in the
environment designed by humans bring benefits to society, as
well as cause risks. Students should understand the costs and
trade-offs of various hazards—ranging from those with
minor risk to a few people to major catastrophes with major risk
to many people. The scale of events and the accuracy with which
scientists and engineers can (and cannot) predict events are
important considerations.
|

|






