America's Stone Age Explorers
|  |
Student Handout
|
The Hunt for mtDNA
You are a forensic scientist recruited to help solve a long-standing "missing
persons" case. Mitochondrial DNA, or mtDNA for short, is the key to your
success.
Procedure
Read the Guidelines for mtDNA Inheritance. Take careful notes as your teacher describes the important elements of
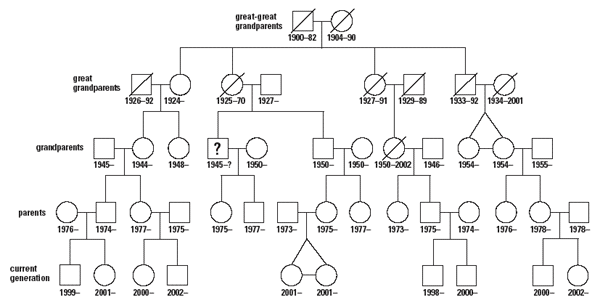
the "Case of the Missing Dung Beetle Biologist." Identify which family members
in the Who's Related by mtDNA? pedigree chart should be chosen to donate
their mtDNA for comparison with the missing person's mtDNA (the missing person
is noted by a question mark). All deceased individuals have been cremated and
cannot be sampled for mtDNA. Connect individuals who share mtDNA from the great-great grandmother by
darkening the lines that link them to one another. Of the individuals connected by dark lines, circle the living relatives who
are eligible to be tested for mtDNA.
Questions
Write
your answers on a separate sheet of paper.
How many living relatives could provide mtDNA to test against the mtDNA of
the discovered remains that are believed to belong to the missing person shown
by a question mark in the pedigree chart? Describe the inheritance pattern of mtDNA. If two brothers died in a crash, could you use mtDNA to distinguish their
remains one from the other? Why or why not? How far back could you trace a lineage of mtDNA?
Who's Related by mtDNA?
 Guidelines for mtDNA Inheritance
Guidelines for mtDNA Inheritance
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is found in each cell's mitochondria, structures that
produce ATP, the cell's main energy source. Here are some guidelines about how
mtDNA is inherited:
- mtDNA can only be inherited from a woman.
- A man can inherit mtDNA from a woman.
- A man cannot pass mtDNA on to any children.
| 