Judgment Day: Intelligent Design on Trial
|  |
Student Handout
|
The Chromosome Shuffle
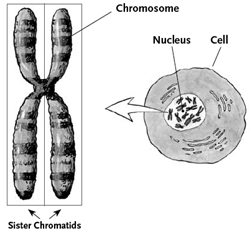
Chromosomes contain all of our
genetic code. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes that exist in nearly every
cell in the body. As part of natural genetic changes over time, chromosomes are
rearranged in a number of different ways, including inversions, deletions,
translocations, fission, and fusion.
These
mutations usually happen during the first prophase of meiosis, when sister
chromatids twist around—or cross over—each other, and can lose,
gain, or exchange parts to produce the kind of mutations shown here.
Procedure
Label the following parts on the
chromosome pictured.
Telomere: At the ends of each chromosome
are telomeres that help determine how many times a normal cell divides.
Telomeres contain a unique repeating sequence of TTAGGG. Called tandem repeats,
these show up 800 to 1,600 times in each telomere.
Centromere: The constricted region of the
chromosome where two sister chromatids are joined and where spindle fibers
attach. The centromere is essential for the division of the chromosome in the
cell.
p arm: The p arm is the shorter arm of the chromosome.
q arm: The q arm is the longer arm of the chromosome.
The following
idiograms—graphic representations of chromosomes—show only one half
of the matched chromosome pair.
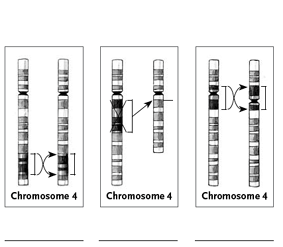
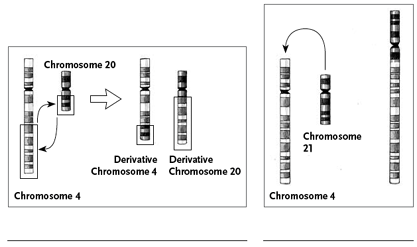
Read about each type of mutation
below, and then write in the space under each set of chromosome drawings which
type of change the drawing depicts. Not all definitions are pictured.
deletion: A segment of a chromosome is lost. Deletion of a gene or part of a gene can lead to a disease
or abnormality.
duplication: A segment of a chromosome is duplicated on the same
chromosome.
fission: A chromosome piece breaks apart, forming two
shorter chromosomes.
fusion: Two different chromosomes are joined.
inversion (paracentric): A segment within just one arm (not including the
centromere) of a chromosome is turned upside down.
inversion (pericentric): A segment containing both the centromere region and
parts of both arms of a chromosome is turned upside down.
translocation (reciprocal): Two chromosomes trade pieces with one another.
|
