January 1 Allied nations sign declaration of the United Nations. January 15 "Resettlements" from Lodz to the extermination camp Chelmno begin. January 20 Wannsee Conference held to solidify plans for the deportation and extermination of European Jewry (Final Solution). Heydrich convened the meeting to transfer mass murders to the fixed death camps, with Eichmann in charge of transportation. January 31 Einsatzgruppe A reports the liquidation of 229,052 Jews in the Baltic states. [Liquidation in this instance means to kill, while liquidation of ghettos usually refers to outright killing and/or deportation to death camps.] End January Deportation of Jews to Theresienstadt begins. February-March Mass murder of Jews in Charkow (Kharkov), Ukraine (14,000 victims). March 1 Extermination of Jews begins at Sobibor, an extermination camp in Poland. By October 1943, 250,000 Jews will have been murdered there. March 6 First conference on sterilization held: Definitions pertaining to sterilization of persons of mixed blood laid down. March 16-17 Extermination camp Belzec established in Poland to murder Jews from Lublin, the Lublin district, and Galicia. By liberation (two survivors), 600,000 Jews had been murdered there. Mid-March Start of "Aktion Reinhard," code name for the operation that had as its objective the physical destruction of Jews in the interior of occupied Poland.
"Resettlement" of the ghetto in Lublin: 26,000 persons sent to extermination camps Belzec and Majdanek and other camps. March 26 Public notices pertaining to the identification of Jewish homes in Germany. Deportation of 60,000 Slovakian Jews, some to Auschwitz, others to the extermination camp Majdanek, near Lublin, Poland. Starting end of March Arrival of initial transports of Jews at the concentration and extermination camps at Auschwitz (Auschwitz I & Auschwitz II). April 24 Jews prohibited from using public transportation. Exception only for forced laborers, if their workplace lies farther than seven kilometers from their place of residence, though taking a seat in the conveyance not allowed. May 27 Czech commandos mortally wound SS leader Heydrich. June 1 Introduction of the Star of David in France and Holland. Treblinka extermination camp opened about 40 miles northeast of Warsaw. June 2 Deportation of German Jews to Theresienstadt begins. June 4 Heydrich dies of his wounds. June 10 Germans liquidate Lidice, Czechoslovakia, in retaliation for Heydrich's death. June 30 Jewish schools in Germany closed. July 1 Massacres of Jews in Minsk, Lida, and Slonim, all in Belorussia.
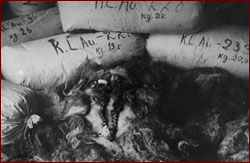
Berlin Jews are sent to Theresienstadt. July 4 Start of mass gassings at Auschwitz. July 7 Himmler grants permission for sterilization experiments at Auschwitz. July 15 First deportation from Holland to Auschwitz. July 19 Himmler orders Operation Reinhard, the mass deportation of Jews in Poland to extermination camps. "Resettlement" of the inhabitants of the Warsaw Ghetto to the extermination camps at Belzec and Treblinka begins. By September 13, Nazis will have deported 300,000 Jews to Treblinka. Armed resistance during liquidation of Nieswiez ghetto, western Belorussia. July 23 Mass exterminations by gassing started at Treblinka. By August 1943, Nazis will have murdered 700,000 Jews there.
First deportations from Belgium to Auschwitz. August 9 Armed resistance during the liquidation of the Mir ghetto, western Belorussia. August 10-22 "Resettlement" of the Lemberg (Lvov) ghetto in Ukraine. Forty thousand Jews deported to extermination camps. August 14 Arrest of 7,000 "stateless" Jews in unoccupied France. August-September Deportations from Zagreb, Croatia, to Auschwitz. Gassings near Minsk of Jews deported from Theresienstadt. September 3 Armed resistance during liquidation of Lahava ghetto, western Belorussia. September 9 Massacre of Jews near Kislowodsk, Caucasus. September 16 Conclusion of "resettlement" of the Lodz ghetto (55,000 victims). September 23 Armed resistance during the liquidation of the Tutzin ghetto, western Ukraine. September 30 Hitler publicly repeats his forecast of the destruction of Jewry. October 4 Nazis order German concentration camps to be made "free of Jews": all Jewish inmates deported to Auschwitz.
The German Ministry of Justice transfers responsibility for Jews and citizens of German-occupied eastern countries to the Gestapo. October 22 Nazis suppress revolt by Jews at Sachsenhausen assigned for deportation to Auschwitz. October 27 Second conference pertaining to sterilization held. October 29 Mass execution of Jews in Pinsk, Belorussia (16,000 victims). November 25 First deportation of Jews from Norway to Auschwitz. December 10 First transport of Jews from Germany arrives at Auschwitz. December 17 Allies solemnly condemn the extermination of Jews and promise to punish the perpetrators. Continue: 1943 Photos: Courtesy of the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum Archives. The Director's Story | Timeline of Nazi Abuses Results of Death-Camp Experiments: Should They Be Used? Exposing Flawed Science | Resources Transcript | Site Map | Holocaust on Trial Home Editor's Picks | Previous Sites | Join Us/E-mail | TV/Web Schedule About NOVA | Teachers | Site Map | Shop | Jobs | Search | To print PBS Online | NOVA Online | WGBH © | Updated October 2000 |