 |
 |
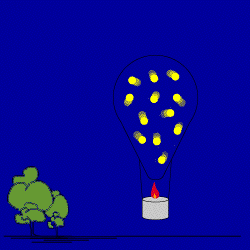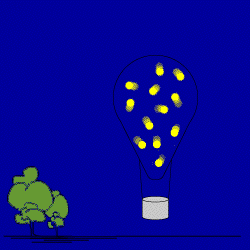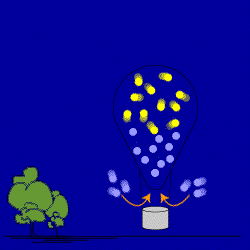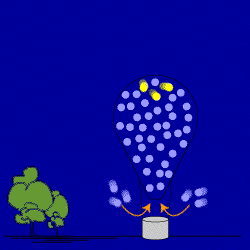 OK, the burner has been cut. The air in the balloon starts to cool. The air
molecules start to slow down, and move closer to each other. Air from outside
moves into the balloon to fill up this extra space. Scientists would say that
you create a partial vacuum inside the balloon which causes the movement of air.
This is why people say "Nature abhors a vacuum!" The density of
the balloon starts to go back to the density of the air
around it because the balloon's mass is increasing. The cooling hot air balloon
loses its ability to float—its buoyancy—and starts to sink.
OK, the burner has been cut. The air in the balloon starts to cool. The air
molecules start to slow down, and move closer to each other. Air from outside
moves into the balloon to fill up this extra space. Scientists would say that
you create a partial vacuum inside the balloon which causes the movement of air.
This is why people say "Nature abhors a vacuum!" The density of
the balloon starts to go back to the density of the air
around it because the balloon's mass is increasing. The cooling hot air balloon
loses its ability to float—its buoyancy—and starts to sink.Ready to use your knowledge of density to take a trip in a hot air balloon? Take the Balloon Challenge! Global Contenders '97/'98 | Expedition '96/'97 | Fossett | Virtual Flight Science of Ballooning | Teacher's Guide | Resources | Transcript | Balloon Home Editor's Picks | Previous Sites | Join Us/E-mail | TV/Web Schedule About NOVA | Teachers | Site Map | Shop | Jobs | Search | To print PBS Online | NOVA Online | WGBH © | Updated October 2000 |